In today's rapidly evolving landscape of building and utility installation, HDD, or Horizontal Directional Drilling, has emerged as a groundbreaking technique that not only improves project effectiveness but also reduces ecological impact. As construction needs increase, especially in city areas, the need for creative approaches like HDD becomes increasingly clear. This underground methodology facilitates the seamless placement of multiple services, including water, gas, and telecommunications, without the extensive excavation commonly needed.
Understanding how HDD works, from the first planning stages to the completion of a job, is essential for experts seeking to improve outcomes. This method provides many benefits over traditional trenching, particularly in sensitive environments or challenging terrains. When we delve into the details of HDD, including its advantages, challenges, and upcoming trends, it is evident that this technology is transforming how we handle service installation and maintenance in our localities.
Comprehending Horizontal Directional Drilling
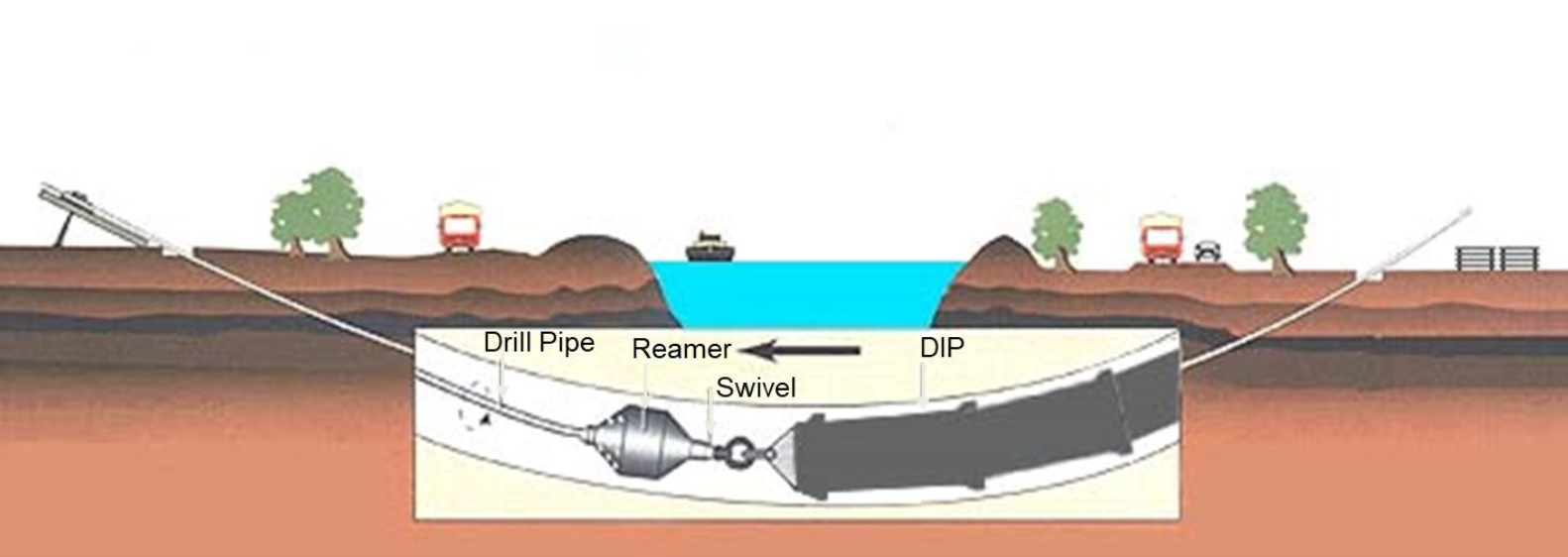
Directional Boring, commonly known as Horizontal Directional Drilling, is a trenchless technique utilized for installing subsurface lines such as lines, wires, and tubes. This modern method allows for the installation of infrastructure with low surface disruption, maintaining the integrity of current buildings and environments. HDD employs a drill that generates a tunnel along a planned route, enabling the setup of different utilities in a exact manner without the requirement for extensive earthwork.
The HDD method begins with the boring of a initial opening, guided by a positioning tool that monitors the boring machine's placement. After the test hole is established, it is often enlarged using a enlarging device to fit the infrastructure being laid. This process is particularly helpful in metropolitan environments where conventional trenching would result in significant disruptions to vehicles and nearby facilities. By using HDD, project managers can effectively navigate through difficult terrains, making it suitable for street and river passages, as well as areas with sensitive ecological factors.
A different key quality of HDD is its potential to reduce environmental impact. Unlike conventional methods, which can produce large trenches and disrupt the surrounding environment, HDD keeps the ground above the surface, significantly minimizing dirt displacement and rehabilitating sites more efficiently. As industries continue to seek more sustainable construction methods, HDD stands out as a popular option for many utility setups, especially in areas where ecological laws are tight.
Advantages and Applications of HDD
Horizontal Directional Drilling offers a variety of advantages that make it a preferred solution for multiple applications. More helpful hints of the primary benefits is its ability to install utilities with minimal disruption to the above-ground conditions. In contrast to traditional trenching methods, HDD allows for the installation of cables and pipelines without significant excavation, thereby preserving existing structures, landscaping, and roadways. This is especially beneficial in urban areas where real estate is scarce and inconvenience to commuters and businesses can result in expensive setbacks.
Moreover, HDD is flexible suitable for various applications, including the laying of water and sewer pipelines, telecom infrastructure, and renewable energy infrastructure. The skill to work in difficult environments, such as rivers or roads, without the need for extensive surface disruption makes it an increasingly popular option. As a result, as awareness of ecological issues heightens, HDD's low-impact approach is becoming essential for projects in environmentally sensitive regions, ensuring that natural habitats remain largely undisturbed.
The effectiveness of HDD also contributes to reduced project timelines and savings in expenses. With the capability to drill long distances in a single attempt, HDD reduces the need for frequent rearrangements and interruptions associated with conventional trenching. This efficiency not only shortens the project duration but also decreases expenses for workforce and restoration. As businesses strive to find creative answers to construction challenges, HDD stands out as an efficient and dependable technique that supports sustainable development initiatives.
Future Trends and Advancements in HDD
The future of HDD is poised for significant progress as technology keeps to evolve. One major development is the growing use of automated systems and intelligent technologies during the boring process. This includes the combination of mechanized steering systems that enhance precision and minimize the chances of human error. Additionally, advancements in data analytics are enabling project managers to refine drilling paths based on real-time feedback, which not only improves efficiency but also improves safety protocols.
Another emerging trend in HDD is the increasing focus on eco-friendliness. As laws around environmental impacts tighten, HDD is increasingly recognized for its low-impact installation capabilities. Future innovations are expected to involve the creation of more sustainable drilling fluids and materials to further minimize ecological disruption. Companies are seeking ways to incorporate renewable energy sources in Horizontal Directional Drilling operations, making the process greener and more eco-friendly in the future.
In conclusion, the demand for HDD in emerging infrastructure projects is growing, especially in city settings where space is limited. Advancements in equipment, such as compact and powerful drilling rigs, are being developed to navigate complex terrains effectively. These developments not only make HDD more adaptable but also position it as the favored choice for essential installations like fiber-optic cables and sustainable energy solutions. As the industry embraces these advancements, the potential to revolutionize infrastructure development keeps on to grow.
